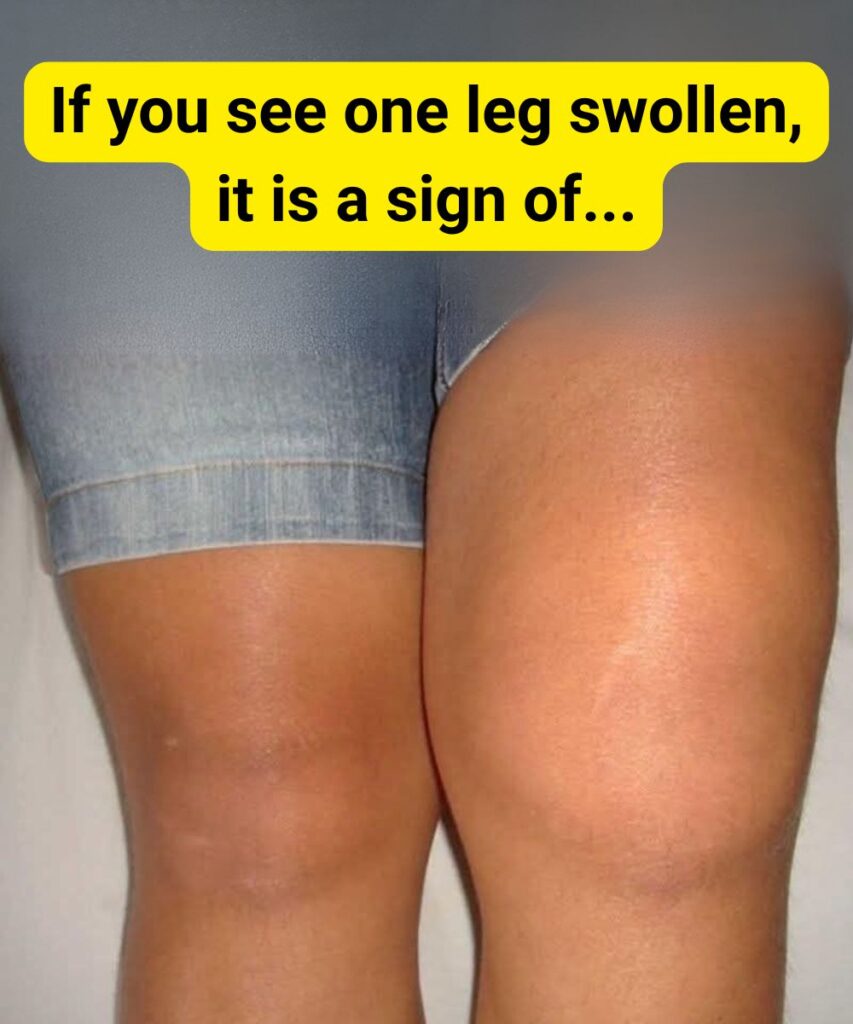
Why Is Only One Knee Swollen?
Noticing swelling in just one knee while the other remains normal can feel concerning. When both knees swell, it often signals a whole-body (systemic) issue like arthritis. However, swelling limited to one knee usually points to a localized problem. Knowing what might cause one swollen knee can help you figure out whether it’s a minor concern or something needing medical care.
1. Injury or Trauma
The most common reason for one swollen knee is injury. Sometimes the cause is obvious, like a fall or sports mishap, but other times, repeated stress or minor strains can lead to swelling without a clear incident. Potential injuries include:
Ligament sprains or tears (like ACL or MCL injuries)
Meniscus tears
Dislocation of the kneecap (patellar dislocation)
Bone bruises or fractures
Typically, swelling appears quickly and may come with pain, stiffness, or a feeling of instability.
2. Bursitis
Bursae are small fluid-filled sacs that cushion the knee joint. If one becomes irritated from pressure, impact, or frequent kneeling, it can cause prepatellar bursitis—often called “housemaid’s knee.” This condition usually affects only one knee, leading to swelling and tenderness at the front of the joint.
3. Infection
An infection inside the knee joint (septic arthritis) is serious and demands urgent care. Symptoms often include rapid swelling, redness, warmth, and intense pain, along with fever or chills. Treatment usually involves draining infected fluid and antibiotics.
4. Gout or Pseudogout
4. Gout or Pseudogout
Sudden, severe knee swelling might be due to a crystal-induced arthritis like gout or pseudogout. Gout happens when uric acid crystals build up in a joint, while pseudogout involves calcium crystals. Both can cause intense pain and swelling in one knee at a time, sometimes recurring in flare-ups.
5. Localized Osteoarthritis
Although osteoarthritis often affects both knees, it can start in only one—especially if there’s a history of prior injury or extra strain on that joint. Swelling from osteoarthritis tends to be mild to moderate and may worsen with physical activity.
6. Baker’s Cyst
A Baker’s cyst is a fluid-filled pocket that develops behind the knee, often linked to conditions like arthritis or cartilage tears. It can cause a feeling of tightness or visible swelling, particularly when bending or straightening the leg.
7. Blood Clot or Circulatory Problems
While less common, a blood clot (deep vein thrombosis) in the leg can cause swelling around the knee, especially if it’s accompanied by calf pain, warmth, or redness. This is a medical emergency requiring immediate attention.
When to See a Doctor
Seek medical care if:
Swelling comes on suddenly and severely, or you develop a fever
Your knee feels hot, red, or extremely tender
You can’t walk, bend, or bear weight on the knee
Swelling persists for more than a few days without getting better
Final Thoughts
Having one swollen knee isn’t always a sign of a serious problem—but it’s definitely worth investigating. From injuries to infections or joint disorders, many conditions could be responsible. Getting a proper diagnosis is the key to effective treatment and maintaining healthy knees for the long term.